Migraine therapy and CGRP receptor, illustration - stock illustration
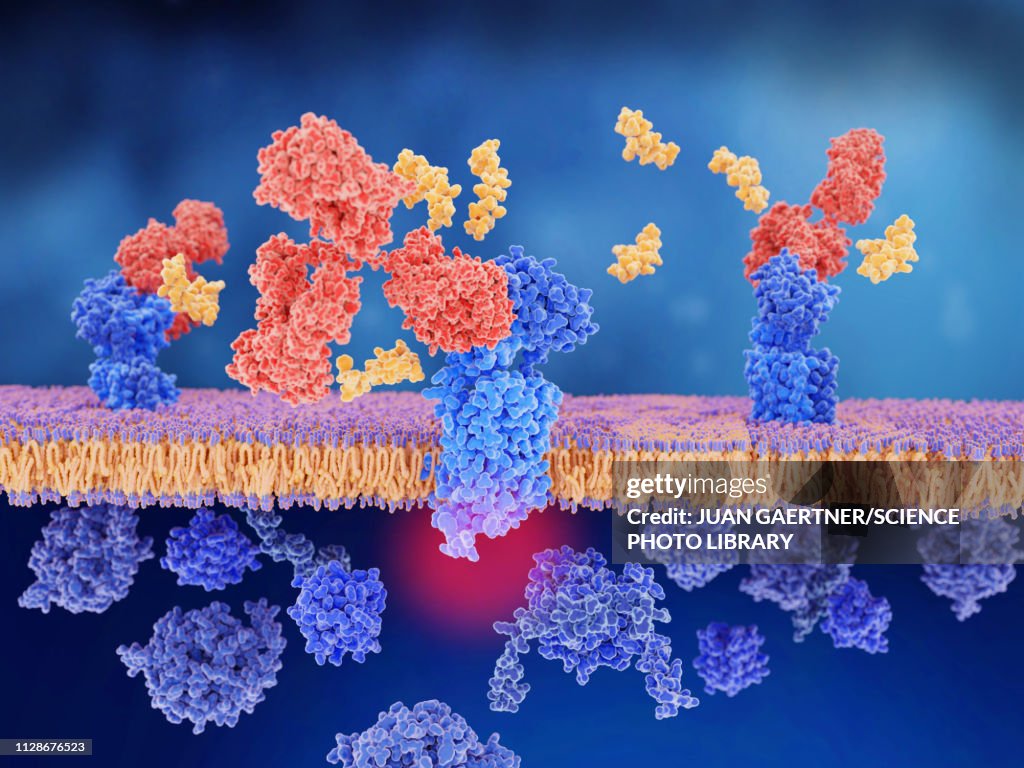
Migraine therapy and CGRP receptor, illustration. Monoclonal antibodies (red) being used to block the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor (blue). The calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, yellow) is designed to bind to its receptor (blue). This occurs on the membranes of neurons and smooth muscle cells in cerebral (brain) blood vessels, activating a signal cascade through G-proteins (dark blue, bottom) that leads to a dilatation of brain blood vessels (vasodilatation). This is a factor in disorders such as migraines. Blocking the CGRP receptor reduces the number of migraine attacks.
Get this image in a variety of framing options at Photos.com.
PURCHASE A LICENCE
All Royalty-Free licences include global use rights, comprehensive protection, and simple pricing with volume discounts available
AED 1,850.00
AED
DETAILS
Creative #:
1128676523
Licence type:
Collection:
Science Photo Library
Max file size:
8000 x 6000 px (67.73 x 50.80 cm) - 300 dpi - 10 MB
Upload date:
Release info:
No release required
Categories:
- Receptor,
- Headache,
- Antibody,
- Atherosclerosis,
- Pain,
- Brain,
- Protein,
- Aura,
- Biochemistry,
- Biological Cell,
- Illustration,
- Three Dimensional,
- Artistic Product,
- Biology,
- Blood Vessel,
- Bonding,
- Cell Membrane,
- Cerebellum,
- Colour Image,
- Digitally Generated Image,
- Healthcare And Medicine,
- Horizontal,
- Microbiology,
- No People,
- Peptide,
- Science,
- The Human Body,
- Trigeminal Nerve,